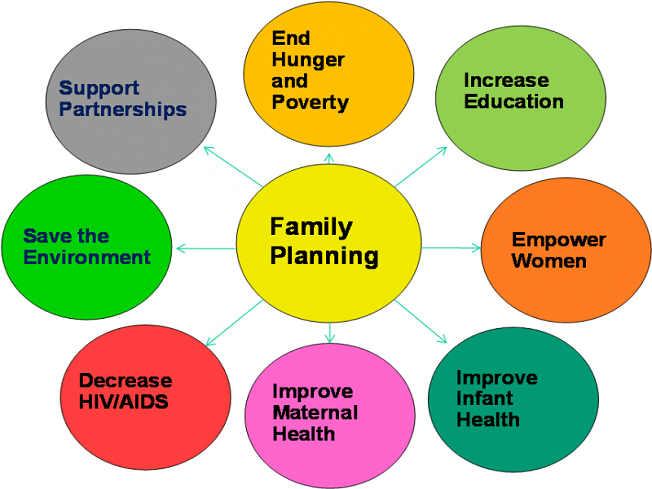
Family planning allows people to
attain their desired number of children and determine the spacing of
pregnancies. It is achieved through use of contraceptive methods and the
treatment of infertility.
Benefits of family planning
Well-being and autonomy of women,
while supporting the health and development of communities.
Preventing pregnancy-related
health risks in women
A woman’s ability to choose if
and when to become pregnant has a direct impact on her health and well-being.
Family planning allows spacing of pregnancies and can delay pregnancies in
young women at increased risk of health problems and death from early
childbearing. It prevents unintended pregnancies, including those of older
women who face increased risks related to pregnancy. Family planning enables
women who wish to limit the size of their families to do so. Evidence suggests
that women who have more than 4 children are at increased risk of maternal
mortality. (WHO)
By reducing rates of unintended
pregnancies, family planning also reduces the need for unsafe abortion.
Reducing infant mortality
Family planning can prevent
closely spaced and ill-timed pregnancies and births, which contribute to some
of the world’s highest infant mortality rates. Infants of mothers who die as a
result of giving birth also have a greater risk of death and poor health.
Helping to prevent HIV/AIDS
Family planning reduces the risk
of unintended pregnancies among women living with HIV, resulting in fewer
infected babies and orphans. In addition, male and female condoms provide dual
protection against unintended pregnancies and against STIs including HIV.
Empowering people and enhancing
education
Family planning enables people to
make informed choices about their sexual and reproductive health. Family
planning represents an opportunity for women to pursue additional education and
participate in public life, including paid employment in non-family
organizations. Additionally, having smaller families allows parents to invest
more in each child. Children with fewer siblings tend to stay in school longer
than those with many siblings.
Reducing adolescent pregnancies
Pregnant adolescents are more
likely to have preterm or low birth-weight babies. Babies born to adolescents
have higher rates of neonatal mortality. Many adolescent girls who become
pregnant have to leave school. This has long-term implications for them as
individuals, their families and communities.
Slowing population growth
Family planning is key to slowing
unsustainable population growth and the resulting negative impacts on the
economy, environment, and national and regional development efforts.
To access our broad range of family planning method/Services visit any of our clinic nationwide.